Prioritize educating yourself before making a diamond purchase. Familiarize yourself with the 4Cs – cut, colour, clarity, and carat – understanding how they influence the diamond's lustre, sparkle, quality, and pricing.
Carat
There is often confusion between Carat and Size in diamonds. Carat signifies the weight, while Size denotes the measurement of the stone in millimeters.
For example, a 1ct diamond with a deep cut may appear the size of an 0.80ct stone, although it still weighs 1ct. Conversely, a 1ct diamond with a shallow cut might appear the size of a 1.25ct stone, while its weight remains 1ct due to its shallowness. A well-cut diamond will both look and weigh as a 1ct.
When diamonds are poorly cut, either too shallow or too deep, they lose brilliance and may appear dark or lacking in the centre in some instances.

Clarity
Diamond clarity is determined by the presence or absence of imperfections, known as inclusions, and their location within the stone. GIA categorizes diamond clarity using the following chart:
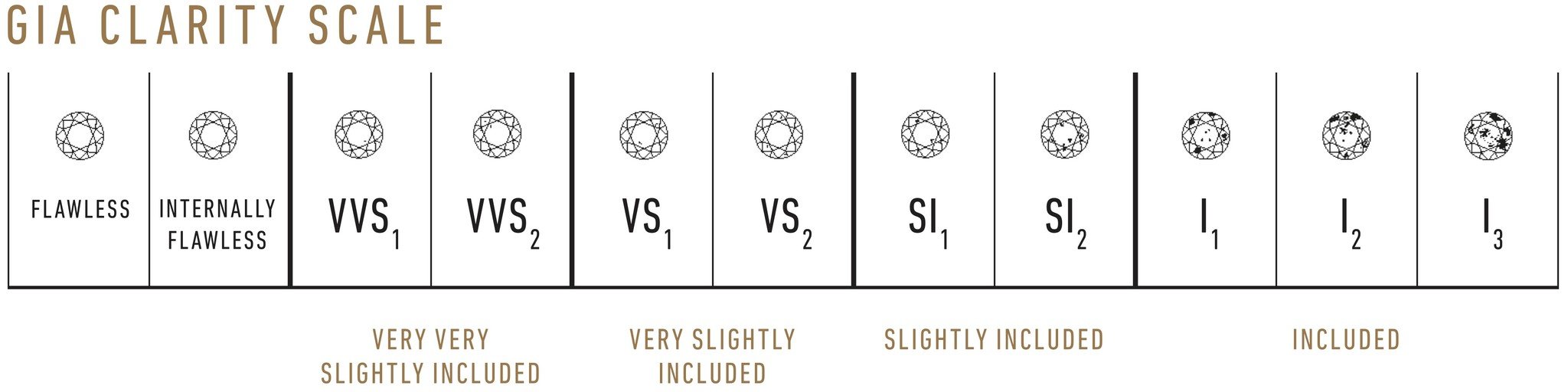
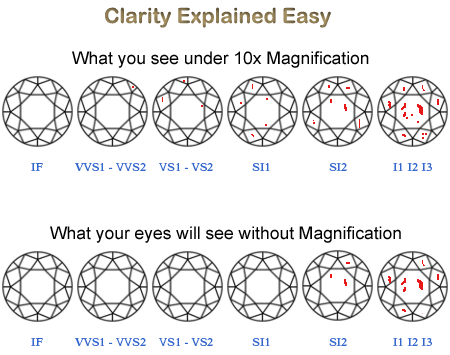
Refer to the following diagram to get an idea of what you will see from the naked eye.
Colour
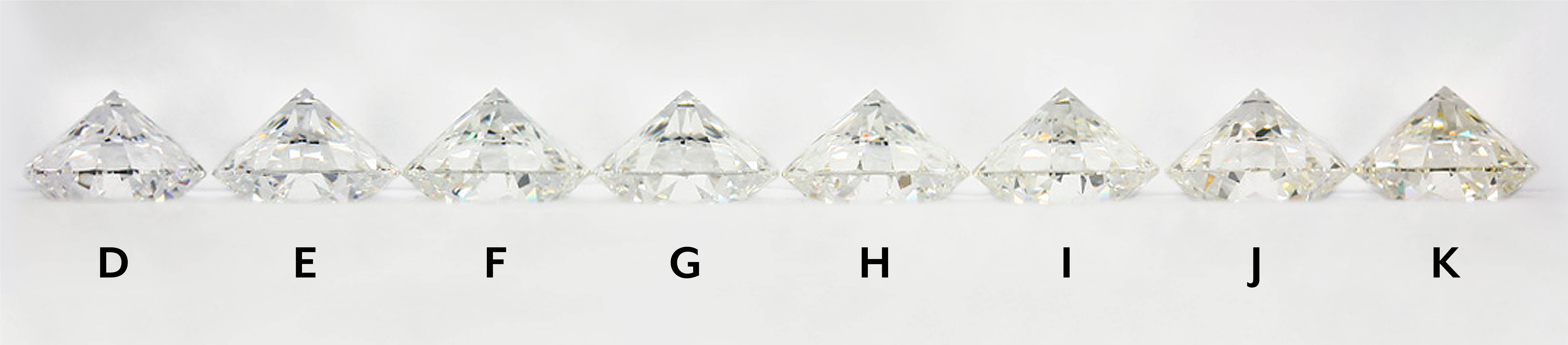
Diamond colour indicates the degree of colourlessness in a stone, with clearer (whiter) diamonds being more valuable. As you descend the colour scale, diamonds exhibit increased colour, like subtle tints of yellow or brown, diminishing their value. The GIA diamond chart assigns grades from D (colourless) to Z (light yellow or brown), categorizing diamonds into various groups.

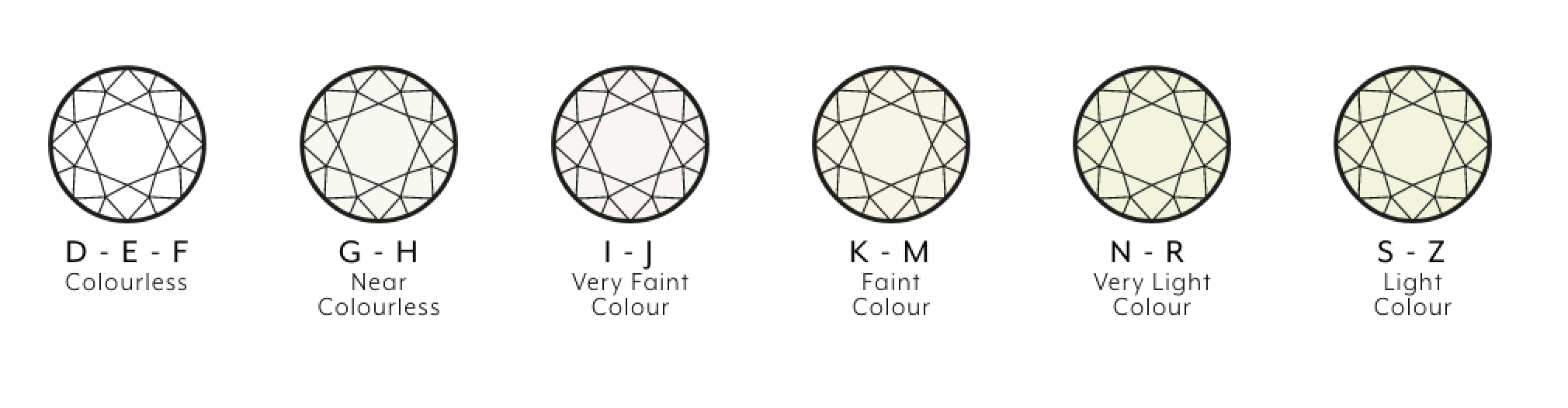
D, E, F (Colourless):
Diamonds graded D-F fall into the colourless category, representing the rarest and highest grade of diamonds. When set, they appear identical to the untrained eye. To discern differences, these stones need to be loose and compared against each other on a white background. They are exceptionally clear, bright, and free of yellow tints.
G, H (Near Colourless):
Diamonds graded G-H are classified as near colourless. They possess a very faint tint of colour that is not easily noticeable without close examination. In a setting, they tend to appear predominantly white. However, when compared to colourless diamonds in a loose state, a subtle tint becomes evident.
I, J (Very Faint Colour):
Diamonds graded I-J are categorized as having a very faint colour. These diamonds exhibit a slight yellow, brown, or grey tint compared to diamonds in the colorless category. Diamonds below a J color may display a more noticeable tint in the stone.
To an untrained eye, diamonds with a 1 or 2 colour difference may appear quite similar.
Cut
The Cut of a diamond stands out as the most crucial aspect among the 4Cs. It profoundly influences a diamond's visual appeal, determining the level of sparkle, fire, and brilliance it will exhibit. If a diamond is not well-proportioned, being either too deep or too shallow, light entering the stone may escape through the bottom instead of reflecting back up, leading to a loss of diamond brilliance. Well-cut diamonds allow light to enter, reflect off all facets, and return straight up, resulting in a scintillating appearance. Even a diamond of exceptionally high quality can appear lacklustre without a top-notch cut grade.
Our Recommendation: Opt for a stone with an Excellent to Ideal Cut.